Coordinative Efforts for Epidemic Prevention and Control and
Economic and Social Development Delivered Notable Results
Decline of Major Economic Indicators
Significantly Narrowed Down in March
National Bureau of Statistics of China
April 17, 2020
In the first quarter of 2020, faced with the severe test of the COVID-19 outbreak, under the strong leadership of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC) with comrade Xi Jinping as the core, all regions and departments strictly implemented the decisions and arrangements made by the CPC Central Committee and the State Council, and the whole nation coordinated efforts to advance both the prevention and control of the epidemic and the economic and social development. As a result, the situation of epidemic control and prevention continued to improve with a basic interruption in epidemic transmission at home. The resumption of work and production accelerated, with fundamental industries and major products vital to national economy and people’s livelihood growing steadily. People’s basic livelihood was well guaranteed and the national economic and social development witnessed overall stability.
According to the preliminary estimates, the gross domestic product (GDP) of China was 20,650.4 billion yuan in the first quarter of 2020, a year-on-year decrease of 6.8 percent at comparable prices. By industry, the value added of the primary industry was 1,018.6 billion yuan, down by 3.2 percent; that of the secondary industry was 7,363.8 billion yuan, down by 9.6 percent; and that of the tertiary industry was 12,268.0 billion yuan, down by 5.2 percent.
1. Overall agricultural production was steady and grains grew well.
In the first quarter, the value added of agriculture (crop farming) grew by 3.5 percent year-on-year. With favorable climate conditions in major farming areas at present, spring plowing and sowing went on smoothly, and winter wheat grew better than last year and average years. By the end of March, the sown area of grade Ⅰand grade Ⅱ seedling of winter wheat accounted for 87.2 percent of the total, 3.5 percentage points higher than that of the same period last year. In the first quarter, the output of eggs grew by 4.3 percent, and that of milk grew by 4.6 percent. The output of pork, beef, mutton and poultry was 18.13 million tons. The pig production capacity continued to get recovered. By the end of the first quarter, 321.20 million pigs were registered in stock, up by 3.5 percent over the end of the fourth quarter of 2019, among which, 33.81 million were breeding sows, up by 9.8 percent.
2. Industrial production dropped while industry of basic raw materials and high-tech manufacturing maintained growth.
In the first quarter, the total value added of the industrial enterprises above the designated size went down by 8.4 percent year-on-year. Specifically, in March, the total value added of the industrial enterprises above the designated size went down by 1.1 percent year-on-year, or 12.4 percentage points slower than the decline of the first two months, while the month-on-month growth was 32.13 percent, with the industrial output approaching the level of the same period last year. An analysis by types of ownership showed that the value added of the state holding enterprises dropped by 6.0 percent year-on-year; that of share-holding enterprises down by 8.4 percent; that of enterprises funded by foreign investors or investors from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan down by 14.5 percent; and that of private enterprises down by 11.3 percent. In terms of sector, the value added of mining went down by 1.7 percent, manufacturing down by 10.2 percent and the production and supply of electricity, thermal power, gas and water down by 5.2 percent. The production of basic raw materials and new products maintained growth. The output of natural gas, non-woven fabrics, chemical medicine materials, crude oil, ten kinds of nonferrous metal, ethylene and crude steel went up by 9.1 percent, 6.1 percent, 4.5 percent, 2.4 percent, 2.1 percent, 1.3 percent and 1.2 percent respectively. The output of automatic vending and ticket machines, electronic components, integrated circuits, urban rail vehicles and solar cells went up by 35.3 percent, 16.2 percent, 16.0 percent, 13.1 percent and 3.4 percent respectively. In March, the high-tech manufacturing went up by 8.9 percent year-on-year, among which, the manufacturing of computers, communication equipment and other electronic equipment went up by 9.9 percent. The output of industrial robots and power generation equipment went up by 12.9 percent and 20.0 percent respectively.
3. Service production dropped while emerging service industry grew well.
In the first quarter, the total value added of the tertiary industry dropped year-o- year, while that of the information transmission, software and information technology services and that of financial intermediation went up by 13.2 percent and 6.0 percent respectively. In March, the Index of Services Production dropped by 9.1 percent, 3.9 percentage points slower than the decline of the first two months. In the first two months, the business revenue of service enterprises above the designated size dropped by 12.2 percent, among which, that of internet and related services and that of software and information technology services went up by 10.1 percent and 0.7 percent respectively. In March, the Business Activity Index for services was 51.8 percent, 21.7 percentage points higher than last month. Specifically, the Business Activity Index for transportation, storage and post, retail trades and monetary and financial services was relatively high, reaching 59.3 percent, 60.6 percent and 62.9 percent respectively. In terms of market expectation, the Business Activities Expectation Index for service was 56.8 percent, 17.1 percentage points higher than last month, showing greater confidence of enterprises for market development.
4. Market sales decreased while sales of daily necessities and online retail sales of physical goods grew fast.
In the first quarter, the total retail sales of consumer goods reached 7,858.0 billion yuan, down by 19.0 percent year-on-year. In March, the total retail sales of consumer goods reached 2,645.0 billion yuan, down by 15.8 percent, a decline narrowed by 4.7 percentage points compared to that of the first two months. The retail sales of goods went down by 12.0 percent, a decline narrowed by 5.6 percentage points compared to that of the first two months. Analyzed by different areas, the retail sales in urban areas in the first quarter reached 6,785.5 billion yuan, down by 19.1 percent, and the retail sales in rural areas stood at 1,072.5 billion yuan, down by 17.7 percent. Grouped by consumption patterns, the income of catering was 602.6 billion yuan, down by 44.3 percent; and the retail sales of goods were 7,255.3 billion yuan, down by 15.8 percent. Commodities closely related to people’s lives witnessed growth. The grain, oil and food, beverages and traditional Chinese and western medicines by businesses above the designated size grew by 12.6 percent, 4.1 percent and 2.9 percent respectively, or 2.9 percentage points, 1.0 percentage point and 2.7 percentage points higher than the growth in the first two months. The online retail sales reached 2,216.9 billion yuan, down by 0.8 percent year-on-year. Specifically, the online retail sales of physical goods were 1,853.6 billion yuan, up by 5.9 percent, 2.9 percentage points higher than that of the first two months, accounting for 23.6 percent of the total retail sales of consumer goods, 2.1 percentage points higher than that of the first two months.
5. Investment growth slowed down while e-commerce, professional technical services and anti-epidemic related industries witnessed growth.
In the first quarter, the investment in fixed assets (excluding rural households) reached 8,414.5 billion yuan, down by 16.1 percent year-on-year, 8.4 percentage points slower than the decline of the first two months. Specifically, the investment in infrastructure, manufacturing, and real estate development declined by 19.7 percent, 25.2 percent and 7.7 percent respectively, 10.6 percentage points, 6.3 percentage points and 8.6 percentage points slower than the decline of the first two months. The floor space of commercial buildings sold reached 219.78 million square meters, down by 26.3 percent; and the total sales of commercial buildings were 2,036.5 billion yuan, down by 24.7 percent, the decline of which was narrowed by 13.6 percentage points and 11.2 percentage points compared to that of the first two months respectively. By industry, the investment in the primary industry went down by 13.8 percent; the secondary industry down by 21.9 percent; the tertiary industry down by 13.5 percent; and the private investment reached 4,780.4 billion yuan, down by 18.8 percent. The decline was narrowed by 11.8 percentage points, 6.3 percentage points, 9.5 percentage points and 7.6 percentage points respectively compared to that of the first two months. The investment in high-tech industry declined by 12.1 percent, 4.0 percentage points slower than that of the total investment. Of the total, the investment in high-tech manufacturing and high-tech services went down by 13.5 percent and 9.0 percent respectively. In terms of high-tech manufacturing, the investment in manufacturing of computer and office equipment grew by 3.2 percent. In terms of high-tech services, the investment in e-commerce services went up by 39.6 percent, that in professional technical services up by 36.7 percent, and that in services for commercialization of research findings up by 17.4 percent. The investment in social sectors went down by 8.8 percent, among which, the investment in health sector dropped by 0.9 percent, or 15.2 percentage points slower than the decline of the total investment. Investment in manufacturing of biological medicines and products and other anti-epidemic related industries maintained growth, and construction of key projects for epidemic prevention accelerated. In March, the investment in fixed assets (excluding rural households) grew by 6.05 percent month-on-month.
6. Imports and exports of goods slowed down and trade structure continued to optimize.
In the first quarter, the total value of imports and exports of goods was 6,574.2 billion yuan, down by 6.4 percent year-on-year. In March, the total value of imports and exports was 2,445.9 billion yuan, down by 0.8 percent year-on-year, a decline slowed by 8.7 percentage points compared to that of the first two months. Of the total, the value of exports was 1,292.7 billion yuan, down by 3.5 percent; the value of imports was 1,153.2 billion yuan, up by 2.4 percent, with import of general trade growing by 4.0 percent. In the first quarter, the total value of exports was 3,336.3 billion yuan, down by 11.4 percent; the total value of imports was 3,238.0 billion yuan, down by 0.7 percent. The trade balance was 98.3 billion yuan in surplus. The trade structure continued to optimize. The import and export of general trade accounted for 60.0 percent of the total value of the imports and exports, an increase of 0.4 percentage points compared with the same period last year. In the first quarter, the export delivery value of industrial enterprises above the designated size reached 2,408.2 billion yuan, down by 10.3 percent year-on-year, 8.8 percentage points slower than the decline of the first two months. In March, the export delivery value of industrial enterprises above the designated size reached 1,030.7 billion yuan, up by 3.1 percent.
7. Growth of consumer price declined and producer prices for industrial products witnessed a larger drop.
In the first quarter, the consumer price went up by 4.9 percent year-on-year. In March, the consumer price went up by 4.3 percent year-on-year, 0.9 percentage points lower than February, or down by 1.2 percent month-on-month. In the first quarter, the price went up by 4.6 percent in urban areas and up by 5.9 percent in rural areas. Grouped by commodity categories, prices for food, tobacco and alcohol went up by 14.9 percent year-on-year; clothing up by 0.2 percent; housing up by 0.2 percent; articles and services for daily use up by 0.2 percent; transportation and communication down by 1.5 percent; education, culture and recreation up by 1.9 percent; medical services and healthcare up by 2.2 percent; other articles and services up by 4.9 percent. In terms of food, tobacco and alcohol prices, prices for grain went up by 0.6 percent; fresh vegetables up by 9.0 percent, specifically, their prices went up by 10.9 percent in February and down by 0.1 percent in March; pork up by 122.5 percent, specifically, its prices went up by 116.4 percent in March, 18.8 percentage points lower than February. Core CPI excluding the price of food and energy went up by 1.3 percent.
In the first quarter, the producer prices for industrial products went down by 0.6 percent year-on-year. Specifically, the prices in March dropped by 1.5 percent year-on-year, 1.1 percentage points faster than the year-on-year decline in the first two months, or down by 1.0 percent month-on-month. In the first quarter, the purchasing prices for industrial producers went down by 0.8 percent year-on-year; specifically in March, the prices dropped by 1.6 percent year-on-year, or down by 1.1 percent month-on-month.
8. Surveyed unemployment rate in urban areas dropped slightly while employment was generally stable.
In the first quarter, the newly increased employed people in urban areas totaled 2.29 million. In March, the surveyed unemployment rate in urban areas was 5.9 percent, 0.3 percentage points lower than that of February. Specifically, the surveyed unemployment rate of population aged from 25 to 59 was 5.4 percent, 0.5 percentage points lower than the surveyed unemployment rate in urban areas, 0.2 percentage points lower than that of last month. The urban surveyed unemployment rate in 31 major cities was 5.7 percent, same as last month. In March, the employees of enterprises worked averagely 44.8 hours per week, 4.6 hours more than last month. By the end of February, the number of rural migrant workers reached 122.51 million.
9. Residents’ nominal income increased while real income decreased and the per capita disposable income ratio between urban and rural households slightly dropped.
In the first quarter, the nationwide per capita disposable income of residents was 8,561 yuan, a nominal increase of 0.8 percent year-on-year, or a real decrease of 3.9 percent after deducting price factors. In terms of permanent residence, the per capita disposable income of urban households was 11,691 yuan, a nominal increase of 0.5 percent, or a real decrease of 3.9 percent. The per capita disposable income of rural households was 4,641 yuan, a nominal increase of 0.9 percent, or a real decrease of 4.7 percent. By sources of income, the nationwide per capita wage income went up by 1.2 percent year-on-year in nominal terms, net operating income down by 7.3 percent, net property income up by 2.7 percent, and net transfer income up by 6.8 percent. The per capita disposable income of urban households was 2.52 times that of the rural households, 0.01 less than that of the same period last year. The median of the nationwide per capita disposable income was 7,109 yuan, down by 0.7 percent.
Generally speaking, the overall national economic and social development in the first quarter maintained stable despite the outbreak of COVID-19. However, we should also be aware that given the continuous spread of the epidemic globally, mounting downward pressure of the world economy, and remarkably increasing instabilities and uncertainties, we are now facing rising pressure of the prevention of imported epidemic infections and new difficulties and challenges for resuming work and production and advancing economic and social development. For the next step, we must fully implement the decisions and arrangements made by the CPC Central Committee and the State Council, further coordinate efforts to advance both epidemic prevention and control and economic and social development, and enhance policies implementation to resume work, production, market and business. We must guarantee and improve people’s livelihood, accelerate the full restoration of production and living order under the normalization of epidemic prevention and control, so as to ensure a decisive victory in building a moderately prosperous society in all respects and achieving poverty alleviation goals.
Notes:
1. The growth rates of gross domestic product, value added of industrial enterprises above designated size and its sub-items are real growth by using comparable prices. The growth rates of other indicators are nominal growth by using current prices unless otherwise specified.
2. According to the auto-revision function of the seasonal adjustment model, revisions were made to quarter-on-quarter growth of GDP and to month-on-month changes of the value added of industrial enterprises above designated size, investment in fixed assets (excluding rural households), and total retail sales of consumer goods. The revised figures, quarter-on-quarter GDP growth for the first quarter of 2020 and month-on-month changes of other indicators for March 2020 are as follows:
The quarter-on-quarter growth of GDP in 2019 and the first quarter of 2020 were 1.6 percent, 1.5 percent, 1.3 percent, 1.5 percent, and -9.8 percent respectively.
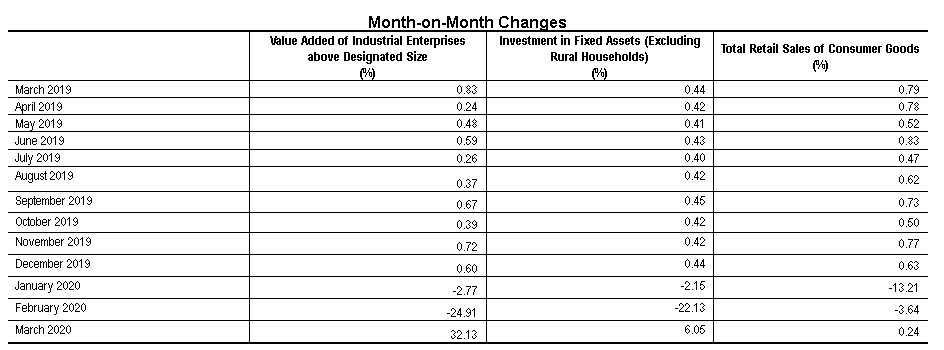
3. Industrial enterprises above the designated size are industrial enterprises with annual revenue from principle business over 20 million yuan.
As industrial enterprises above the designated size change every year, to ensure the data comparability between years, the coverage of the data of the same period last year used for estimating year-on-year growth rates like that of products output, are as consistent as possible with the current period and different from the coverage of the data published last year. The main reasons are as follows: First, the statistical units change. Every year, some enterprises are included in the survey as they meet the threshold, while some enterprises are removed from the survey because of downsizing. Besides, enterprises that have newly gone into operation, been bankrupted, canceled their registrations or had their business licenses revoked also cause impact. Second, duplicated outputs across regions of enterprise groups have been removed based on the ad hoc surveys since duplication was found in the products output of some enterprise groups.
4. The Index of Services Production is the change of production in the reporting period compared to the base period with the price factors deducted.
5. The scope of the total retail sales of consumer goods include all legal entities, establishments and self-employed individuals involved in retail trades or providing catering services. Specifically, businesses above the designated size include wholesale enterprises (businesses), retail enterprises (businesses) and lodging and catering enterprises (businesses) with annual revenue from principal business over 20 million yuan, 5 million yuan and 2 million yuan respectively.
As the wholesale, retail, and lodging and catering enterprises (businesses) above the designated size change every year, to ensure the data comparability between years, the coverage of the data of the same period last year used for estimating year-on-year growth rates like that of the retail sales of consumer goods by businesses above the designated size is consistent with the current period and different from the coverage of data published last year. The main reasons are as follows: every year, some enterprises (businesses) are included in the survey as they meet the threshold, while some enterprises (businesses) are removed from the survey because of downsizing. Besides, enterprises (businesses) that have newly gone into operation, been bankrupted, canceled their registrations or had their business licenses revoked also cause impact.
Online retail sales refer to the retail sales of goods and services realized through internet trading platforms (including self-built websites and third-party platforms). Goods and services include physical goods and non-physical goods (e.g. virtual goods and services).
The total retail sales of consumer goods include the online retail sales of physical goods, but not the non-physical goods.
Data of the total retail sales of consumer goods in 2019 are revised according to the results of the fourth national economic census. Monthly growth rate in 2020 is calculated on a comparable basis.
6. The data of investment in fixed assets of the same period last year are revised according to the results of the fourth national economic census, the statistical law enforcement and inspection, and the regulations of statistical programs. The growth rates are calculated on a comparable basis.
7. Employed people refer to people aged 16 and above who have the ability to work and engage in gainful employment for remuneration payment or business income.
8. The median of the nationwide per capita disposable income of residents refers to the per capita disposable income of households which lies in the middle of all surveyed households ranked from low to high on the basis of per capita disposable income level.
9. Data of imports and exports are from the General Administration of Customs; and data of newly increased employed people in urban areas are from the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security.
10. Due to the round-off reasons, the subentries may not add up to the aggregate totals.
In case of any differences between English translation and the original Chinese text, the Chinese edition shall prevail.