Medical and Health Services in China
Information Office of the State Council
The People’s Republic of China
December 2012, Beijing
Foreword
Good health is a prerequisite for promoting all-round development of the person. And it is a common pursuit of human societies to improve people’s health and ensure their right to medical care. For China, a large developing country, medical and healthcare is of vital importance to its population of over 1.3 billion, and is a major issue concerning its people’s well being.
China pays great attention to protecting and improving its people’s health. As the Constitution stipulates, “The state develops medical and health services, promotes modern medicine and traditional Chinese medicine..., all for the protection of the people’s health.” Based on this constitutional stipulation, China has put in place a complete system of laws and regulations concerning medical and health services.
Over the years, China has worked hard to develop its medical and health services with Chinese characteristics in accordance with the policy of “making rural areas the focus of our work, putting disease prevention first, supporting both traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine, relying on science, technology and education, and mobilizing the whole of society to join the efforts, improving the people’s health and serving socialist modernization.” Thanks to unremitting efforts that have been made, medical and healthcare systems covering both urban and rural residents have taken shape, the capabilities of disease prevention and control have been enhanced, the coverage of medical insurance has expanded, continuous progress has been made in medical science and technology, and the people’s health has been remarkably improved.
To put into place basic medical and healthcare systems covering both urban and rural residents, and ensure that every resident has access to safe, effective, convenient and affordable basic medical and health services, China has kept advancing the reform of its medical and healthcare system, and made important achievements in the current stage.
I. Basic Conditions
The people’s health has been improved. Judging from important indicators that give expression to national health, the health of the Chinese people is now among the top in developing countries. In 2010, the life expectancy was 74.8 years - 72.4 years for males and 77.4 years for females; the maternal mortality rate went down from 51.3 per 100,000 in 2002 to 26.1 per 100,000 in 2011; the infant mortality rate and the mortality rate of children under the age of five have kept dropping, with the former going down from 29.2 per thousand in 2002 to 12.1 per thousand in 2011, and the latter, from 34.9 per thousand to 15.6 per thousand, attaining ahead of schedule the UN Millennium Development Goal in this regard.
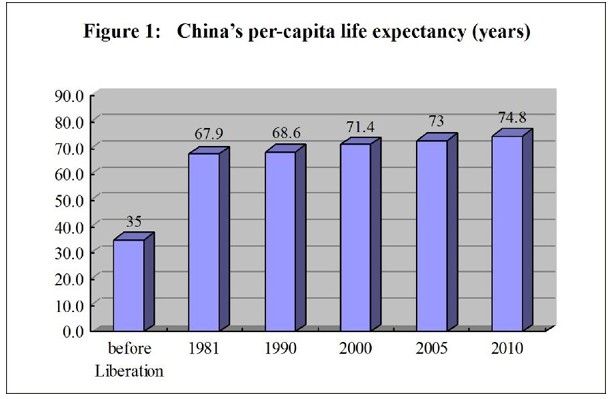
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 1: China's per-capita life expectancy (years), according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012. Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 1: China's per-capita life expectancy (years), according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
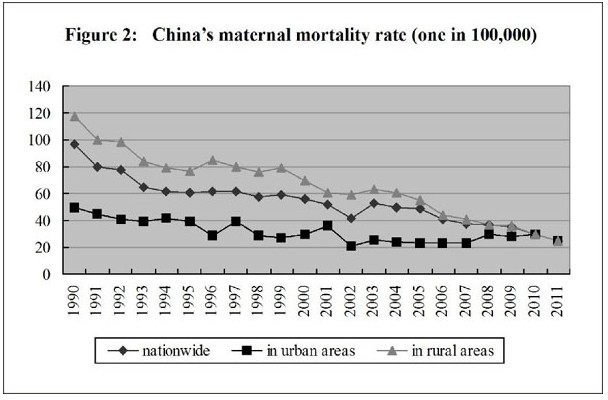
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 2: China's maternal mortality rate (one in 100,000) from 1990 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012. Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 2: China's maternal mortality rate (one in 100,000) from 1990 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
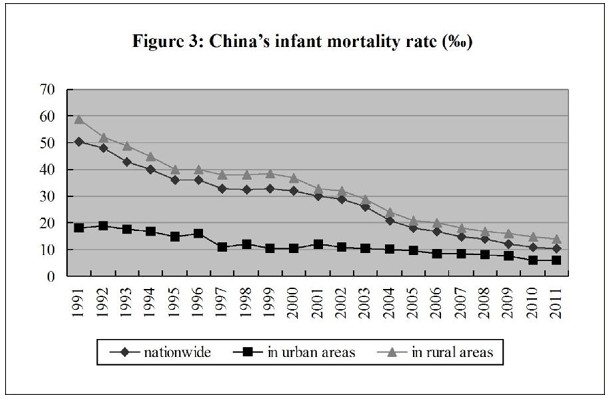
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 3: China's infant mortality rate from 1991 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 3: China's infant mortality rate from 1991 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
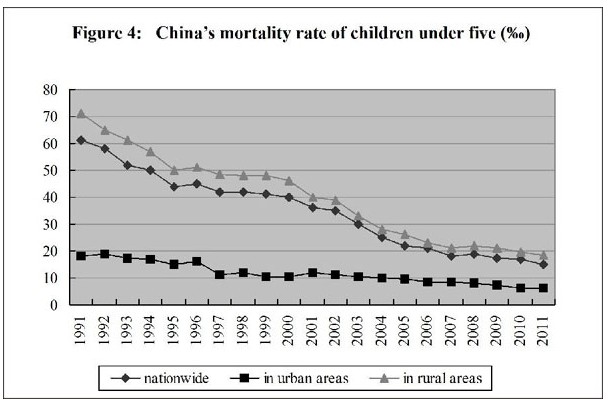
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 4: China's mortality rate of children under five years of age from 1991 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012. Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 4: China's mortality rate of children under five years of age from 1991 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
Medical and healthcare systems covering both urban and rural residents have been put in place. Of these systems, the first is the public health service system, which covers disease prevention and control, health education, maternity and child care, mental health, health emergency response, blood collection and supply, health supervision, family planning and some other specialized public health services, and a medical and healthcare system based on community-level healthcare networks that provides public health services. The second is the medical care system. In the rural areas, it refers to a three-level medical service network that comprises the county hospital, the township hospitals and village clinics, with the county hospital performing the leading role, and township hospitals and village clinics service at the base. And in the cities and towns, it refers to a new type of urban medical health service system that features division of responsibilities as well as cooperation among various types of hospitals at all levels and community healthcare centers. The third is the medical security system. This system comprises mainly the basic medical security, supported by many forms of supplementary medical insurance and commercial health insurance. The basic medical security system covers basic medical insurance for working urban residents, basic medical insurance for non-working urban residents, a new type of rural cooperative medical care and urban-rural medical aid, which cover, respectively, the employed urban population, unemployed urban population, rural population and people suffering from economic difficulties. And the fourth is the pharmaceutical supply system, which covers the production, circulation, price control, procurement, dispatching and use of pharmaceuticals. The recent work is focused on establishing a national system for basic drugs.
The health financing structure has been constantly improved. China’s health expenditure comes from the government’s general tax revenue, social medical insurance, commercial health insurance, residents’ out-of-pocket spending, etc. In 2011, the total health expenditure in China reached 2,434.591 billion yuan, 1,806.95 yuan per capita. The total expenditure accounted for 5.1% of the country’s GDP. In comparable prices, the health expenditure grew by an average annual rate of 11.32% from 1978 to 2011. Individual “out-of-pocket” spending declined from 57.7% in 2002 to 34.8% in 2011, showing that health financing is working better in the areas of risk protection and re-distribution. In 2011, the spending on hospitals and outpatient establishments was 1,808.94 billion yuan, and that on public health agencies, 204.067 billion yuan, comprising 71.74% and 8.09%, respectively, of the total health expenditure. Of the total spending on hospitals, those on urban hospitals, county hospitals, community health service centers and township health service centers stood at 64.13%, 21.28%, 5.17% and 9.3%, respectively.

Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 5: China's total health expenditure and its proportion of the GDP from 1978 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012. Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 5: China's total health expenditure and its proportion of the GDP from 1978 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
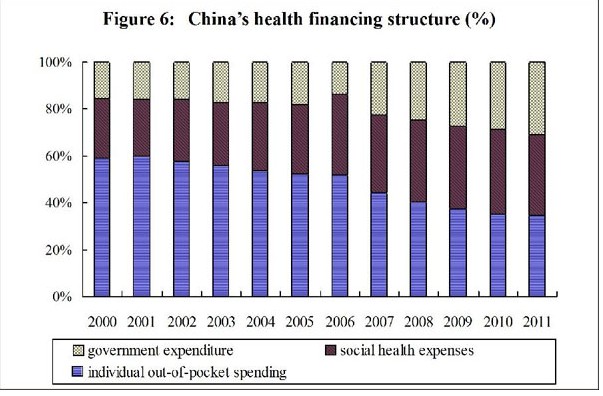
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 6: China's health financing structure (%) from 2000 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 6: China's health financing structure (%) from 2000 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
Health resources have been developing in a sustained way. By the end of 2011, medical and healthcare institutions around the country totaled 954,000, an increase of 148,000 over 2003. Licensed doctors (assistants) reached 2,466,000, or 1.8 per thousand people, as compared with 1.5 per thousand people in 2002. Registered nurses totaled 2,244,000, or 1.7 per thousand people, as compared with one per thousand people in 2002. The number of hospital beds reached 5160,000, or 3.8 per thousand people, as compared with 2.5 per thou-sand people in 2002.
Marked improvement has been seen in the utilization of medical and health services. In 2011, medical institutions throughout the country hosted 6.27 billion outpatients, as compared with 2.15 billion in 2002; and admitted 150 million inpatients, as compared with 59.91 million in 2002. That year, Chinese residents went to the medical institutions for medical treatment 4.6 times on average; 11.3 of every 100 people were hospitalized; the utilization rate of hospital beds reached 88.5%; and the hospital stay of the inpatients averaged 10.3 days. These figures show that it has become increasingly convenient to see a doctor and more easily accessible to get medical services. In 2011, 83.3% of all households (80.8% in rural areas) could reach medical institutions within 15 minutes, as compared with 80.7% in 2002. Medical service quality management and control systems have been constantly improved. A system of blood donation without compensation has been established, so as to ensure blood supply and safety.
II. Reform of Medical and Healthcare Systems
With years of effort, China has made remarkable achievements in the development of its healthcare undertakings, which, however, still fall far short of the public’s demands for healthcare as well as the requirements of economic and social development. Especially when China turned from a planned economy to a market economy, the old medical care system has undergone great changes. So it became an issue of major importance for the Chinese government to provide better and more accessible medical and health services to the public. In the 1980s, the Chinese government initiated reform of the medical and healthcare systems, and speeded up the reform in 2003 after a success was won in the fight against the SARS. In March 2009, the Chinese government promulgated the “Opinions on Deepening Reform of the Medical and Health Care Systems,” setting off a new round of reform in this regard. The basic goal of this reform was to provide the whole nation with basic medical and health services as a public product, and ensure that everyone, regardless of location, nationality, age, gender, occupation and income, enjoys equal access to basic medical and health services. And the basic principles to be followed in the reform were to ensure basic services, improving such services at the grass-roots level and establishing the effective mechanisms.
Medical reform is a social program that covers a wide range and involves difficult tasks. And it is a hard and complicated task to deepen this reform in China, a developing country with a large population, low per-capita income and a wide gap between urban and rural areas. For over three years, the Chinese government has worked hard to strike a balance between improving medical and health services on one hand and economic and social development on the other, trying to find a solution to this worldwide problem. Thanks to the persistent efforts made, China has made positive progress in this new round of medical reform.
The basic medical care systems cover both urban and rural residents. By 2011, more than 1.3 billion people had joined the three basic medical insurance schemes that cover both urban and rural residents, i.e., the basic medical insurance for working urban residents, the basic medical insurance for non-working urban residents, and the new type of rural cooperative medical care, with their total coverage being extended from 87% in 2008 to 95% in 2011. This signaled that China has built the world’s largest network of basic medical security. Medical care financing and the reimbursable ratio of medical costs have been raised, and the government subsidy standards for the new rural cooperative medical care system were increased from 20 yuan at the beginning to 200 yuan per person per year in 2011, benefiting 1.315 person/times in 2011 as against 585 person/times in 2008. The reimbursement rate for hospitalization expenses covered by relevant policies has been raised to around 70%, and the range of reimbursable expenses has been expanded to include outpatient expenses. Real-time reimbursement has been adopted for medical expenses, making it more convenient for people to have their medical costs settled. Reform has been carried out in respect of the forms of payment to include payment by person, payment by disease and total amount pre-payment, enabling medical insurance to play a better restrictive role over medical institutions as well as to control expenses and compel the medical institutions to improve their efficiency. Critical illness insurance has been included in the new type of rural cooperative medical care system. By 2011, some 230,000 patients of congenital heart disease, advanced rental diseases, breast cancer, cervical cancer, multidrug-resistant tuberculosis and childhood leukemia had been granted subsidies for major and serious diseases, with the actual subsidies accounting for 65% of their total expenses. In 2012, lung cancer, esophagus cancer, gastric cancer and eight other major diseases were included in the rural pilot program of insurance for the treatment of major diseases, and the reimbursement rate reached as high as 90%. Critical illness insurance has been introduced for both urban and rural residents, in which certain amounts of money are earmarked in the medical insurance fund for non-working urban residents and that of the new type of rural cooperative medical care to buy critical illness insurance policies from commercial insurance companies, aiming to relieve urban and rural families of the heavy burden of catastrophic medical spending. The policy of subsidy for critical illness insurance, which covers no less than 50% of the actual medical costs, provides a guarantee for the compliance costs to be shouldered by the individual after reimbursement from the basic medical insurance. This has effectively reduced the financial burden of individuals. An urban-rural medical assistance system has been established and improved, which at first covered urban and rural subsistence allowance recipients and childless and infirm rural residents who receive the so-called “five guarantees,” and is now extended to cover those who are severely ill and have low comes, the severely disabled, senior citizens from low-income families, and some other groups with special difficulties. In 2011, the urban-rural medical assistance was granted to 80.90 million cases across the country.
A basic system of drugs has been developed from scratch. A system for the selection, production, supply and use of basic drugs, and cover of them in medical insurance has been put into place. In 2011, the coverage of this system was extended to all grass-roots medical and health-care institutions run by the government, where these drugs were sold at zero profit, practically eliminating the practice of hospitals subsidizing their medical services with drug sales. A national guideline for the clinical application of basic drugs and a formulary have been drawn up to ensure that basic drugs are used according to due procedures at grass-roots medical institutions. A new mechanism has been established for the procurement of basic drugs, under which the basic drugs are to be purchased by provinces. As a result, the prices of basic drugs at grass-roots medical and healthcare institutions have dropped by 30% on average, as compared with those before the reform. The basic drugs have all been included in the list of reimbursable drugs covered by basic medical insurance. Also, efforts have been made to supply basic drugs in an orderly way to village clinics and non-governmental medical institutions at the grass-roots level. The steps of reform have been quickened in drug production and circulation, and the supply of drugs has been better ensured.
Urban and rural grass-roots level medical and health services have been further improved. The government has invested more to ensure the funding for grass-roots medical and healthcare institutions. From 2009 to 2011, the central government invested 47.15 billion yuan to support the building and development of grass-roots level medical institutions. Diverse forms have been adopted to strengthen the ranks of healthcare workers at the grass-roots level, and preferential policies have been made to train and introduce competent personnel for rural and community healthcare. A system of general practitioners (medical workers with sufficient knowledge in all branches of medicine) has been established, under which general practitioners are trained in the regular way; grass-roots medical and healthcare workers are enrolled in training courses for upgrading them to general practitioners; and medical students are specially trained for the needs of central and western urban areas, for which they do not have to pay their tuition fees. A project, known as “ten thousand doctors extending support to rural medical care,” has been launched. From 2009 to 2011, over 1,100 Grade-III urban hospitals extended support to 955 rural county-level hospitals every year, and urban medical institutions above Grade II in central and western China granted aid to over 3,600 township hospitals every year, thus helping improve the overall technological level and management of the county and township hospitals. Meanwhile, the mode of medical services has been changed. Touring medical services have been provided in township hospitals; and in the urban districts ranks of general practitioners have been formed and a system of family doctors has been set up. Prevention has been combined with the treatment, measures have been taken to ensure basic needs of the residents to see doctors and make it possible that the diagnosis and treatment of most commonly seen and frequently occurring diseases are performed at the community level. After years of effort, community-level medical and healthcare system has been strengthened; marked changes have taken place to the situation of backward facilities and poor services in rural and remote areas; community-level medical workers have increased in number, and their educational background and knowledge have improved. In 2011, the number of grass-roots medical and healthcare institutions across the country reached 918,000, including 26,000 urban community service centers, 38,000 township hospitals and 663,000 village clinics, and the number of hospital beds reached 1,234,000.
Access to basic public health services has become more equitable. The state provides all residents with a free package of 41 basic public health services in ten categories, including health record, health education, preventive inoculation, healthcare for children under six, healthcare for pregnant and lying-in women, healthcare for elderly people, treatment for hypertension and type II diabetes patients, healthcare for severe psychosis patients, reporting and handling of infectious diseases and public health emergencies, and healthcare supervision and coordination. Targeting special diseases, key groups and special areas, the state has launched key public health service programs, including subsidizing rural pregnant women for hospitalized childbirth, re-vaccinating people under 15 against hepatitis B, eliminating fluorosis caused by coal burning, supplementary taking of folic acid by rural women before pregnancy and in the early stage of pregnancy, building sanitary toilets, cataract removal for poor patients, cervical and breast cancer tests for rural women within eligible age, and preventing mother-to-child transmission of AIDS. In 2011, the inoculation rate of the National Immunization Program (NIP) exceeded 90%; the rate of hospitalized childbirth nationwide reached 98.7% (98.1% in rural areas); and the maternity mortality rate in rural areas kept going down. In the rural areas, 72.1% of the population had access to tap water and 69.2% had access to sanitary toilets. In 2009, the government launched a program to provide cataract operations for a million poor patients, and by 2011 more than 1.09 million such people had had such operations with government subsidies.
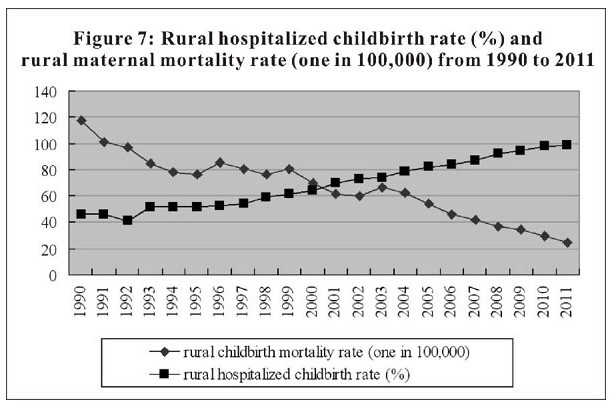
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 7: Rural hospitalized childbirth rate (%) and rural maternal mortality rate (one in 100,000) from 1990 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012. Xinhua
Medical and Health Services in China-Figure 7: Rural hospitalized childbirth rate (%) and rural maternal mortality rate (one in 100,000) from 1990 to 2011, according to a white paper released by the Information Office of the State Council on Dec. 26, 2012.
The reform of public hospitals has been carried on in an orderly way. In 2010, the Chinese government started pilot reforms of public hospitals in 17 state-designated cities and 37 province-level districts; and positive progress has been witnessed in improving services, innovating institutions and mechanisms, strengthening internal management and speeding up the creation of a situation in which hospitals are established and run in diversified forms. In 2012, the government launched a pilot comprehensive reform of county-level public hospitals, aiming to improve rural system of medical services with the county hospitals playing the leading role, and enabling 90% of the population in a county to see doctors. So far, over 600 counties in 18 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government have been included in this reform. The government has worked hard to improve medical services, optimize the allocation of medical resources, and enhance the medical capabilities of weak areas and weak fields. The capabilities of key clinical specialties in regional medical centers and county-level hospitals to deliver medical services have been enhanced, and the mechanism of division of responsibilities and cooperation between public hospitals and community-level medical institutions is being studied and formed. The government has intensified efforts in the creation of a situation of establishing and running hospitals in diversified forms, encouraging and guiding non-governmental funds to establish both for-profit and non-profit medical institutions. By 2011, there were 165,000 medical institutions established with non-governmental investment, including 8,437 private hospitals, accounting for 38% of the national total. Doctor-appointment service, time-phased outpatient service and high-quality nursing service that bring benefits and convenience to the people have been introduced nationwide. The fast price growth of medicine has been contained. In comparable prices, the growth rates of average outpatient and inpatient costs in public hospitals has decreased year by year in the past three years, and that of 2011 went down by eight percentage points from that of 2009, reaping initial results in expense control for public hospitals.
The new round of medical reform has brought substantial benefits to both urban and rural residents. Access to basic public health services has become much more equitable; the gap between urban and rural areas and between regions has been narrowed in medical development; medical services in rural and remote areas with backward facilities and weak capabilities have been remarkably improved; medical services have become more affordable and accessible; and fewer and fewer people are becoming poor or return to poverty because of illness.
III. Infectious Disease Prevention and Treatment, and Health Emergency Management
Since the founding of New China, the Chinese government has persisted in the principle of “prevention first and integrating prevention with treatment” and continuously intensified efforts in the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. By preventive inoculation, patriotic health campaigns and other prevention and control measures, China has succeeded in bringing down the morbidity of infectious diseases and brought their spread under control. China has basically brought under control the epidemics of such diseases as plague, cholera, kala-azar and leprosy since the 1950s. In 2011, the morbidity of Class A and B infectious diseases was kept at a low level - 241.4 per 100,000 people. All these measures help to safeguard the Chinese people’s health and life.
National immunization program has been implemented. The national immunization program represents one of the most notable and influential undertakings of China’s healthcare work. In the early 1960s, China eliminated smallpox through vaccine inoculation, a dozen years ahead before the World Health Organization (WHO) announced the eradication of the disease in 1980. China attained the goal of eliminating poliomyelitis in 2000. In 2002, the Chinese government decided to include hepatitis B vaccination for the newborn in the national immunization program, increasing the number of four vaccines against six infectious diseases to five vaccines against seven infectious diseases. In 2007, China decided to further expand the scope of the program, increasing the number of vaccines to 14 to prevent 15 infectious diseases and extending the scope of vaccination from children to including adults. Since the launch of the new round of medical reform, the scope of the national immunization program has kept expanding, and it has played a positive role in reducing the morbidity of infectious diseases and improving the health of the public. Already, the morbidity of most infectious diseases that can be prevented by vaccination has fallen to the lowest level in history.
Major infectious and endemic diseases have been brought under effective control. Patients of many major infectious diseases, such as AIDS, tuberculosis, snail fever, hydatid disease, leprosy and malaria, are provided medicines and treatment free of charge. In 2011, China’s living HIV-infected persons and AIDS patients were estimated at 780,000, far below China’s goal of controlling the HIV-infected population within 1.5 million. The morbidity of infectious tuberculosis has fallen to only 66 per 100,000 people, attaining the goal defined in the UN Millennium Development Goals ahead of time. All counties where epidemics of snail fever used to break out have attained the goal of bringing under control such epidemics, limiting the number of snail fever patients to 326,000. China took the lead in eradicating filariasis among the 83 countries where epidemics of filariasis hit. China keeps improving its capabilities of influenza control and prevention, taking monitoring at the major task. In 2010, the National Influenza Center of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention was officially nominated the fifth WHO Collaboration Center for Reference and Research on Influenza. China steadily promotes endemic disease prevention and treatment. It has eradicated the diseases caused by iodine deficiency at the national level, and brought under effective control of Kashin-Beck disease, Keshan disease and fluorine poisoning, notably reducing the incidence of these diseases.
Patriotic health campaign has gained fruitful results. Patriotic health campaign, an invention of China that has been in existence for 60 years so far, is a social welfare undertaking featuring massive public participation and a close relationship with the public health. Following the principle of taking prevention first, the campaign has reduced the hazards of infectious diseases and promoted the public health through a series of measures, such as exterminating pests, health education and promotion, improving rural water supply and sanitation, building “healthy cities and towns,” and improving the environmental hygiene in both urban and rural areas. A wholesome atmosphere is taking shape, with everyone participating in the campaign and enjoying a healthy lifestyle. Now, China is exploring a better working mechanism for building “healthy cities and towns,” based on the 153 cities, 32 districts and 456 towns (counties) that have been nominated “healthy” for their wholesome surroundings.
Health emergency management capability has been enhanced. China is striving to make its health emergency management more standard and law-based by issuing the Law on Emergency Management and the Regulations on Preparedness for and Response to Public Health Emergencies, and amending the Law on the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. Based on the disease prevention and control system, the public health monitoring system and the medical service system, China has basically set up a response system for public health emergencies featuring unified leadership, reasonable distribution, quick response, efficient operation and powerful logistics. China has established and improved health emergency plans, which cover the prevention and control of such public health emergencies as acute infectious disease emergencies, diseases with unknown causes and poisoning incidents, medical rescue in case of natural disasters, disastrous accidents and terrorist attacks, and medical services for important events. A four-level emergency management system has been established that covers the national, provincial, city and county levels. Also has been established is the public health emergency response ability assessment system. The central government has organized 27 teams for health emergencies to respond to four categories of incidents, namely, infectious disease control, medical rescue, poisoning treatment, and nuclear and radiation accident handling. Local governments have also set up professional teams to handle health emergencies at their respective levels. China’s medicine reserve system keeps improving, ensuring sufficient supply of medicines for health emergencies. In the past few years, China has successfully dealt with many public health emergencies, especially pandemic threats of infectious diseases, including SARS, H1N1, plague and avian influenza, carried out urgent medical rescues for the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in Sichuan Province, 2010 Yushu earthquake in Qinghai Province and 2010 Zhouqu mudslide in Gansu Province, and provided medical services for the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games and 2010 Shanghai Expo.
Online direct report system has been enforced for notifiable infectious diseases and public health emergencies. The online direct report system, which puts the 39 infectious diseases defined by law and public health emergencies under real-time and online surveillance, was not available in China until 2004. By 2011, the online direct reporting of infectious diseases had been extended to all disease prevention and control institutes, 98% of medical institutions at and above the county level, and 94% of township clinics in China.
IV. Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Non-communicable Disorders
Accelerated industrialization, urbanization and ageing of the population have brought about a trend of a continuous and rapid increase in the incidence of chronic diseases and mortality caused by such diseases. At present, about 260 million Chinese have been diagnosed to have contracted chronic diseases that have caused 85% of total deaths in China and incurred 70% of total medical costs.
The Chinese government regards chronic disease prevention and treatment as an important task in improving the people’s health and well-being. It has established step by step a nationwide prevention and treatment service for chronic diseases, adopted level-by-level management over certain major chronic diseases, implemented a comprehensive control strategy, enhanced the overall prevention and treatment capacity over chronic diseases, made efforts to reduce factors that cause chronic diseases and bring down the morbidity and mortality of chronic diseases as well as disability caused by them.
Integration has been promoted between prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Since 2002, China’s strategy for prevention and control of chronic diseases has gradually shifted to placing equal emphasis on prevention and treatment from laying stress on treatment alone. At the state level, a chronic disease prevention and control system, which takes as its technical support the China Center for Disease Control, the National Cancer Center of China and the National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases of China, has gradually taken shape. In the localities, networks of chronic disease prevention and control have gradually been formed, comprising the local disease control institutions, grass-roots medical and healthcare institutions, hospitals as well as professional prevention and treatment organizations. The principle of early diagnosis and early treatment was proposed, in a bid to realize the targets of reducing the rate of morbidity, mortality and disability in the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases. Primary attention has been directed at the general public, the high-risk population and people with diseases. For major chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, malignant tumors, diabetes and chronic obstructive lung diseases, effective medical interventions should be taken to reduce biological risk factors, like high blood pressure, hyperglycemia, high cholesterol in blood and overweight/obesity, and behavioral risk factors, such as smoking, unhealthy diet, lack of physical exercises and excessive drinking.
Measures for chronic disease control and prevention have been worked out. China has issued the “National Program for Chronic Disease Control and Prevention (2012-2015)” and other relevant policy documents and guidelines. Starting in 2005, such major special programs as that for early diagnosis and early treatment of cancer have been put into implementation. In 2007, a nationwide movement of healthy lifestyle was launched in the general public, employing various measures and channels to encourage the people to cultivate a healthy lifestyle. In 2009, the government included hypertension, diabetes and elders’ health management in the basic public health services amidst medical reform. In 2010, China set out to build state-level demonstration areas in chronic disease prevention and control capacity, aiming at enhancing the comprehensive prevention and control capability against chronic diseases. Comprehensive intervention has been vigorously carried out for early-childhood oral disorders to prevent dental caries among children.
Information management system of chronic diseases has been established. China enforces comprehensive surveillance of chronic diseases, monitors the risk factors of such diseases, the incidence, the causes of death, and nutrition and health conditions of people suffering from these diseases, and has established cancer registries, thereby establishing and gradually improving an information system that centers around chronic diseases and the prevalence of their risk factors, so as to provide scientific basic data for the state’s chronic disease prevention and control efforts.
Health education and promotion movements have been carried out. China will continue to promote the “national health-promotion campaign for farmers,” “healthy community campaign,” “healthy manners promotion campaign,” and other health-promotion campaigns. Efforts will be made to gradually build a health education system featuring cooperation among multiple departments and the whole-society participation. Knowledge of and skills related to health will become increasingly widespread among the Chinese people, and their awareness of good health and ability to keep healthy are being constantly enhanced. Publicity has been intensified for tobacco control to enhance the public’s awareness of the hazards of smoking, and eventually creating the atmosphere that the whole society support tobacco control. Since China joined the WHO Framework Convention of Tobacco Control in January 2006, the various localities in China have made proactive efforts to legalize control of smoking in public places for a smoking-free environment.
Maintenance of people’s mental health has been valued. China issued the Mental Health Law to regulate the mental health services and protect the rights and interests of people with mental disorders. The Chinese government strives to improve the prevention and treatment network of severe mental illnesses, enhance the ability of mental healthcare institutions to treat and cure acute or severe mental illnesses, and has established a working mechanism for severe mental illness prevention and treatment in which psychiatric hospitals and communities support and cooperate with each other. China has included professionals in mental health services as the urgently needed task during the 12th Five-Year Plan, and has intensified their training. It has standardized patient services and management, launched a basic data collection and analysis system for severe mental illnesses, and digitized data on patients. At present, there are 3.026 million people with serious mental disorders in China’s urban and rural areas who are receiving standard management at their homes.
V. Protecting Women and Children’s Right to Health
Currently, China has 860 million women and children, accounting for two thirds of the nation’s total population. The Chinese government has established gender equality as a basic national policy, and has always attached great importance to the life and health of women and children. The state strives to improve the legal regime and related policies regarding women and children’s healthcare, and has signed many international conventions committed to the protection of women and children. China has improved its health services for women and children, and implemented public health service programs for them, focusing on making these services more equitable and accessible so as to effectively protect women and children’s right to health.
The legal regime and related policies regarding women and children’s healthcare have been improved. In October 1994, the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress reviewed and passed the Law on Healthcare for Mothers and Infants, which signaled that China’s management of women and children’s affairs had entered a law-based stage. Since the 1990s, the Chinese government has enacted the Program for the Development of Chinese Women (1995-2000), Program for the Development of Chinese Women (2001-2010), Program for the Development of Chinese Women (2011-2020), Program for the Development of Chinese Children in the 1990s, Program for the Development of Chinese Children (2001-2010) and Program for the Development of Chinese Children (2011-2020), giving priority to women and children’s health in national programs of economic and social development.
The health service system for women and children has been improved. China’s healthcare system for women and children takes professional women and children’s health organizations as its core and is based on community-level urban and rural healthcare services. With technical support from large and medium-sized general hospitals and relevant research and training institutions, the state provides all-round healthcare services for women and children. The country publishes annual reports on women and children’s healthcare progress and has developed the world’s largest monitoring network in this regard, keeping track of cases of birth defects, deaths of pregnant and lying-in women, deaths of children under five years of age, and complicated cases of pregnant and lying-in women, as well as children’s nutrition and health. The information collected on women and children’s health has provided a solid statistical basis for governments at all levels to formulate healthcare policies, especially policies on women and children’s health.
The reproductive health services for women are provided. China has proactively promoted premarital and pre-pregnancy healthcare, and has been publicizing knowledge on prenatal and postnatal care, and reproductive health. Intensive healthcare services for pregnant and lying-in women are available, and a complete array of services for pregnant and lying-in women has been developed, covering prenatal examination, prenatal defect screening and diagnosis, screening and management of high-risk pregnant and lying-in women, hospitalized delivery, infant healthcare and postnatal home visits. In 2011, a total of 93.7%, 91.0% and 85.2% of pregnant and lying-in women, respectively, received prenatal examinations, postnatal home visits and other medical management services in China, 4.81%, 5.57% and 10.36% higher than the statistics of 2000. The percentage of high-risk pregnant and lying-in women included in the medical management program has reached 99.6%. China has carried out a program to “lower the maternal mortality and eliminate neonatal tetanus,” which achieved the desired effects. The maternal mortality rate in 2011 was 26.1 per 100,000, dropping 72.4% and 50.8% as compared to 1990 and 2000, respectively. The state also provides medical services for the screening and treatment of gynecological diseases, adolescence health, and climacteric and old-age health, offering services that cover the whole life cycle of Chinese women.
The healthcare services for children are provided. China has strengthened healthcare for newborns and regularized home-visiting service for newborns. The state offers healthcare services for infants, young children and pre-school children, and exercises health management of children under seven years of age and comprehensive management of children under three years of age. In 2011, some 84.6% of children under three years of age and 85.8% of children under seven years of age received comprehensive health management and medical management services. Chinese children are growing healthier and faster physically, and cases of malnutrition keep declining. The state strives to control birth defects and improve the quality of newborn babies, and has conducted disease screenings for newborns, early development programs for children under three years old, rehabilitation training for children with growth deviation, early-stage intervention for high-risk children, early-stage intervention in cases of food allergy, assistance with sleep problems, early-stage help in case of damage to children’s health caused by environmental pollution, and adolescence healthcare, among others. Children whose parents seek employment away from home, children who live with their migrant-worker parents, disabled children and other special groups of children also receive attention and help from the state both physically and mentally.
VI. Development of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has a long history in China, and is a medical science formed and developed by the Chinese people in their daily work and life as well as attempts to treat diseases. TCM is the crystallization of the wisdom of the Chinese people, and has made important contributions to the continuance and thriving of the Chinese nation. Known for its unique characteristics and advantages in curing common diseases, frequently occurring diseases and complicated diseases, TCM has also proved effective in treating infectious diseases and is very popular among the Chinese public for its low cost, satisfactory curative action and mild side effects. TCM plays an irreplaceable role in China’s medical and healthcare endeavors, and the Chinese government has always supported and promoted its development.
Networks of TCM medical services have been established to cover both urban and rural areas. Networks of TCM medical services now cover Chinese cities, providing services for urban residents through TCM hospitals, ethnic-medicine hospitals, hospitals of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine, specialized TCM hospitals, TCM departments of general hospitals, community health services, TCM outpatient departments and TCM clinics. In the rural areas, TCM service networks have also been developed to serve rural residents through county-level TCM hospitals, and TCM departments or sections of township hospitals and village clinics. Currently, 75.6% of community health service centers, 51.6% of community health service stations, 66.5% of village and township hospitals and 57.5% of village clinics can provide TCM services.
A unique training system for qualified TCM professionals has been developed. The state takes the cultivation of qualified professionals as the cornerstone for the development of TCM. China has enhanced its efforts to pass down the academic achievements and experience of renowned and senior TCM experts as well as the training of high-caliber professionals in clinical practice. An education system for TCM personnel has been basically developed in the forms of academic education, master-apprentice tutorials and continued education at different levels and through different channels. By 2011, China had a total of 46 institutions of higher learning specializing in TCM and ethnic medicine, with 553,000 undergraduate students of TCM on campus, as well as 294,000 practitioners and assistant doctors of TCM, in addition to 97,000 licensed and assistant pharmacists in TCM.
A modernization drive for TCM has been initiated. The state has proactively promoted theoretical and technical innovations in TCM through the application of modern science and technology, and has gained important achievements in basic TCM theory, clinical diagnosis and treatment, TCM technology and other related areas. China promotes the industrialization and modernization of TCM, and as a result the industrial scale and technical level of TCM has increased markedly. Currently, there are about 1,500 manufacturers of TCM pharmaceuticals in China, and the variety, quantity and processing technique of TCM pharmaceuticals have improved by a wide margin. The state attaches importance to the protection of TCM’s cultural values, and 41 TCM programs have been included on the nation’s intangible heritage list.
International exchanges and cooperation have been actively promoted. China has signed treaties with TCM contents or special TCM cooperation agreements with over 70 countries, and cooperation in TCM application in foreign countries, and TCM education and technical cooperation has steadily expanded. Now, over 160 countries and regions around the world have access to TCM. TCM acupuncture and moxibustion has been recognized as a masterpiece of the intangible heritage of mankind, and the Huangdi Neijing (Inner Canon of the Yellow Emperor), Bencao Gangmu (Compendium of Materia Medica) and other TCM treatises have been included in the UNESCO Memory of the World. The International Standardization Organization (ISO) has set up a TCM technical committee and located its secretariat in China.
VII. International Medical and Healthcare Cooperation
For a long period of time, China has been actively participating in international health affairs, and has carried out extensive inter-government and non-governmental multilateral and bilateral cooperation and exchanges. China has also proactively taken part in major health programs of the international community and international organizations. The state pays great attention to international health assistance programs, and has played a huge role in improving the medical and health conditions in many developing countries by building hospitals, training medical and healthcare professionals and carrying out disease control there.
Support has been rendered to the work of the World Health Organization and other international organizations. China has been taking an active role in international discussions on health issues and sharing experiences in this regard. In the 1970s, China summarized its practices in healthcare and played an important part in the signing of the Declaration of Alma-Ata in 1978 on primary healthcare by contributing its medical experience. In recent years, China has been efficiently maintaining timely and close contact with the World Health Organization and various countries under the framework of the International Health Regulations (2005), making its due contribution to disease control on a global scale. The Chinese government makes annual donations to the World Health Organization, the Joint United Nations Program on HIV and AIDS (UNAIDS), the Global Fund to fight AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria, and other international efforts. China also vigorously supports international work to combat chronic diseases and human avian influenza, as well as in tobacco control, emergency medical responses and other related technical fields.
Regional health cooperation has been strengthened. In 2003, China initiated cooperation in the field of infectious disease control with ASEAN, and has quickened its steps to promote regional health cooperation since then. Currently, China is carrying out health cooperation with peripheral countries and regional international aid programs within seven regional cooperation mechanisms, namely, those of the Greater Mekong Sub-region, Central Asia Region, China-ASEAN, ASEAN and China, Japan and Korea, Inter-China-Japan-Korea, Asia-Pacific, and Shanghai Cooperation Organization. Since 2005, China has been cooperating with Myanmar, Vietnam and Laos to carry out joint prevention and control programs of malaria and AIDS, as well as cross-border cooperation programs on the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis and dengue fever.
Medical teams have been sent to developing countries to improve medical conditions there. The medical teams China dispatches to developing countries to improve the medical and health conditions there are a regular aid program between the Chinese government and the recipient countries in accordance with bilateral agreements. In 1963, the Chinese government sent its first medical team abroad, to Algeria, and by 2011, China had sent medical teams to 73 countries. Currently, there are 56 Chinese medical teams in Algeria, Tanzania, Morocco, Zimbabwe and 49 other countries. The medical teams provide free medical services for local people there, especially people in poverty-stricken areas, as well as introducing advanced medical technology into the recipient countries. For 50 years, the Chinese medical teams have diagnosed and treated a total of 260 million cases, and their work has been much appreciated by the people and fully recognized by the governments of the recipient countries. So far, about 900 Chinese medical team members have been awarded honors by the recipient countries, and 50 members died during their service abroad.
Medical institutions have been built in developing countries with aid from China. Since 1970, China has been committed to helping developing countries in Africa and other areas to build medical institutions and improve their medical conditions. By the end of 2011, China had helped a total of 52 countries, and built 100 hospitals and medical centers for them, improving medical conditions and providing medical services for local people. China equipped the hospitals with a large number of complete sets of medical equipment and medicines, and in 2011 alone it shipped 34 batches of medical equipment and medicines to the recipient countries. By November 2011, 31 new projects in this regard were still under construction in 28 countries.
Health professionals have been trained by China for developing countries. The Chinese medical teams pass their medical knowledge and technology to local medics through personal tutorials, lectures and training courses, improving the medical technology of the recipient countries. The Chinese government supports health technology institutions to hold related study and training programs for developing countries in China. By 2011, China had held over 400 training courses for 15,000 persons on health management, emergency management, food hygiene, traditional medicine, infectious disease prevention and control, laboratory testing, health quarantine, nursing skills and other areas. To help developing countries train medical and health professionals of high caliber, China also offers government scholarships for students from developing countries studying medicine and TCM in China.
International emergency rescue has been undertaken. In 2004, Southeast Asia and South Asia suffered great casualties due to an earthquake in the Indian Ocean and the following tsunami. China promptly responded to the emergency by sending medical rescue teams to Thailand, Sri Lanka and Indonesia to help relief efforts there, and donated medical equipment and cash in US dollar to the affected countries through the World Health Organization. Over the past five years, the Chinese government has responded to about 200 health emergencies, sending medical rescue teams to Guinea-Bissau, Madagascar, Pakistan, Indonesia, Haiti and other countries stricken by epidemics or natural disasters, as well as providing relief supplies and cash to those countries. China has also dispatched rescue teams to Lebanon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and other international peacekeeping mission areas to offer humanitarian medical aid there, and its Peace Ark hospital ship sailed to five Asian and African and four Latin-American nations to provide medical services to the people there.
Conclusion
With the quickened pace of the country’s industrialization and urbanization, as well as its increasingly aging population, the Chinese people are facing the dual health threats of infectious and chronic diseases, and the public needs better medical and health services. In the meantime, problems still exist regarding China’s health resources, especially the shortage of high-quality resources and the unbalanced distribution of those resources. China has arduous tasks ahead for reforming and developing its medical and health services.
The Chinese government has announced that it will establish a sound basic medical and health system covering both urban and rural residents by 2020, so as to ensure that everyone enjoys access to basic medical and health services. For this goal, China will continue to reform and develop its medical and health services, and better maintain, ensure and enhance the health of its people. China will also continue its active role in international health affairs and work together with different parties to make greater effort to improve the health of mankind.
