China is stepping up efforts to seek growth impetus from innovation and build its overall strength in science and technology.
In the first half of 2016, a series of remarkable achievements were made in science and technology fields, which in turn have injected new vitality to the economy and profoundly improved social development.
Dark-matter satellite concluded in-orbit test task
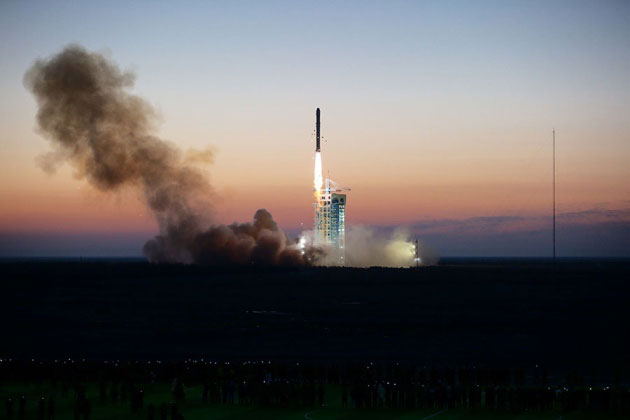

The Monkey King spacecraft, which took to the skies on Dec 17, is designed to detect the high-energy particles produced by annihilating dark matter.[Photo/Xinhua]
China’s first Dark Matter Particle Explorer Satellite “Wukong” completed three months of in-orbit testing in March, with initial findings expected to appear by the end of 2016.
The satellite completed all set tests, with all its technical indicators reaching or exceeding expectation, which may lead to major breakthroughs in cutting-edge scientific fields, according to the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Retrievable space science probe launched
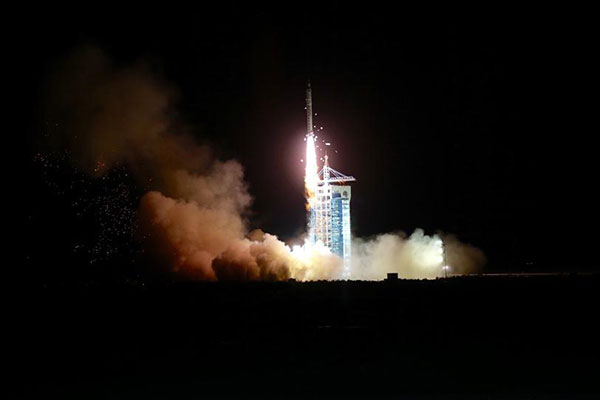

A Long March 2-D rocket carrying the SJ-10 Satellite blasts off at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in Jiuquan, northwest China’s Gansu province, April 6, 2016.[Photo/Xinhua]
China sent a retrievable scientific research satellite into space in April to aid scientists in studying microgravity and space life sciences.
Nineteen experiments will be carried out in the orbital module or in the re-entry capsule to improve scientists’ understanding of oil reservoirs buried deep underground and to help enhance energy efficiency and cut emissions on Earth.
4,500-meter submersible’s maiden dive completed
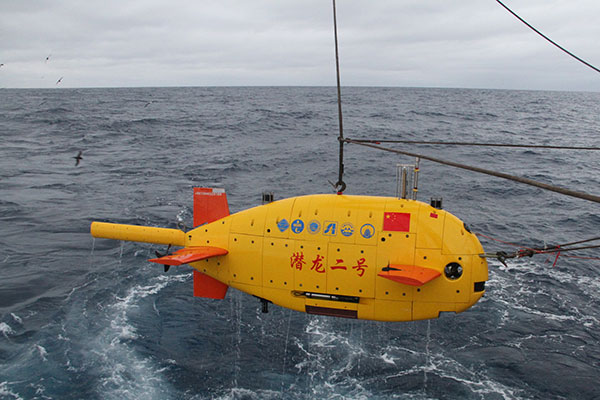
China’s self-developed unmanned autonomous underwater vehicle, Qianlong-2, prepares for undersea exploration on Jan 10, 2016.[Photo/Xinhua]
China’s unmanned submersible Qianlong No 2 completed its maiden dive in the southwest Indian Ocean, the China Ocean Mineral Resources R&D Association revealed in January.
The underwater robot was independently designed by Chinese scientists and can dive to a depth of 4,500 meters. The submersible remained underwater for about nine hours, having explored the area’s landforms, hydrothermal sulfides and magnetism.
First high orbit remote sensing satellite put into use
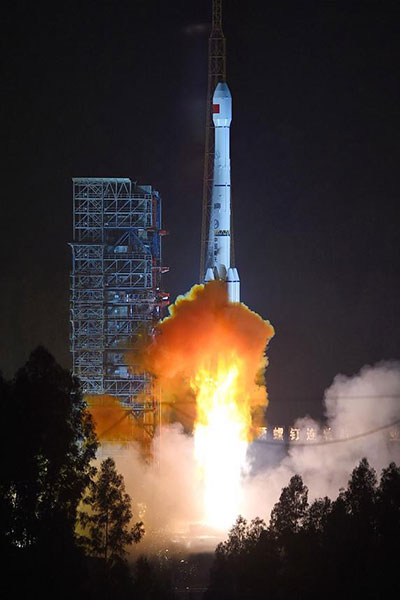

Photo taken on Dec 29, 2015, shows the Long March-3B carrier rocket is launched with the Gaofen-4 Satellite in Xichang of southwest China’s Sichuan province.[Photo/Xinhua]
China’s first high orbit remote sensing satellite, Gaofen-4, went into use after six months of in-orbit testing in June.
Low orbit satellites cannot always follow natural disasters, but Gaofen-4 can continuously observe a disaster. It improves the response to disasters like earthquakes, landslides and typhoons with its high-precision sensors.
Long March-7 rocket nearly ready for maiden launch in Hainan
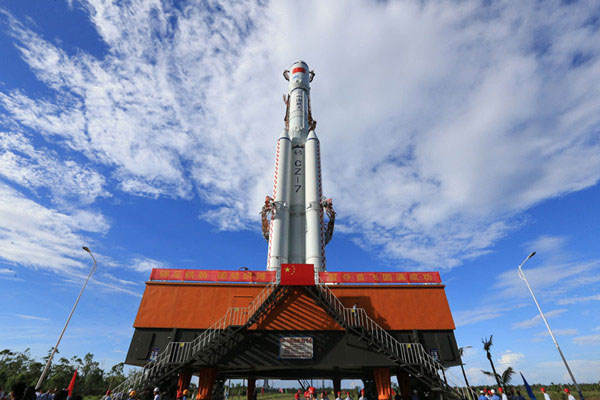

A photo of the Long March-7 carrier rocket is ready for its maiden mission at Wenchang Satellite Launch Center on the northeast coast of Hainan province on June 25.[Photo/Xinhua]
China’s new generation Long March-7 carrier rocket reached the launchpad on June 25. With a breakthrough loading capacity of 18 tons, it is expected to become the main carrier for space launches. There are also many other scientific breakthroughs in the design of the rocket, such as its intense wind resistance, and its waterproof technology.
Sunway-TaihuLight named world’s fastest supercomputer
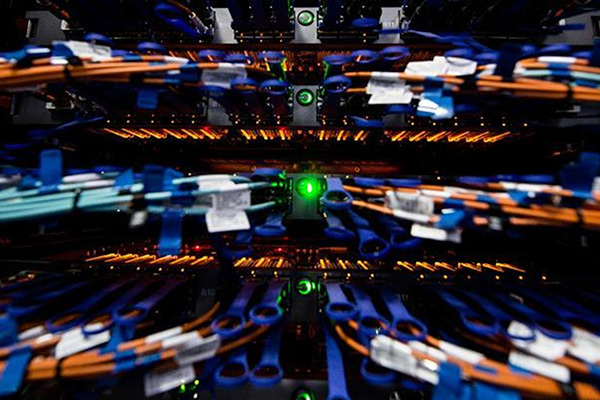

Photo taken on June 16, 2016, shows interchanger cables of Sunway-TaihuLight, a new Chinese supercomputer, in Wuxi, east China’s Jiangsu province.[Photo/Xinhua]
China’s new supercomputing system, Sunway-TaihuLight, was named the world’s fastest computer at the International Supercomputing Conference in Germany on June 20.
According to a professor of computer science at the University of Tennessee, these supercomputers are more important than ever, as they provide the capability to match a broad range of industries, including energy, pharmaceuticals, aircraft, automobile and entertainment and to allow diverse industries to engineer superior new products more quickly.
Looking into the future
China is expected to embrace more sci-tech achievements in the coming months, including a series of China’s aerospace development from the launch of Gaofen-3 remote sensing satellite to Tiangong-2, China ‘s second space laboratory. Also, a much-anticipated Beijing to Shanghai intercity-railway based on the quantum communication network satellite will be built, and an experimental satellite based on quantum science will be launched.
China plan to establish itself as one of the most innovative countries by 2020 and a leading innovator by 2030, before becoming a world-leading science and technology power by 2049.
